In 2002, Freeport LNG Development, L.P. was established to construct an LNG import and regassification terminal at Quintana Island near Freeport, Southern Brazoria County, Texas. In 2008, shortly after the completion of the project, the US Oil & Gas industry experienced a dramatic turnaround in demand vs supply of natural gas, due to abundant supply of Shale Gas.1 The transformation of the facility for LNG export was permitted by the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission (FERC) in July 2014.
The project is spread out on 490 acres of land leased from Port Freeport, 400 acres of pre-treatment land and 650 acres of open land in the Brazosport Area.2 With an investment of over $14 billion, the first 3 trains will have a liquefaction capacity of 13.9 million metric tonnes per annum (MMTPA). A Train 4 expansion project is currently in the Front-End Engineering and Design phase. Delays on account of hurricane Harvey coupled with contractor execution delays, have pushed the start date to mid-2019, with the 2nd and 3rd trains coming into operation in beginning and mid 2020 respectively.3
The fully operational plant is expected to consume two billion cubic feet of feed gas daily, through the interconnected intrastate pipeline systems.4 Sale contracts are already in place for a 20-year supply of 13.4 MMTPA of LNG to Osaka Gas, JERA (an alliance between Tokyo Electric and Chubu Electric), BP Energy, ENN Energy Holdings and SK E&S. Another 20-year contract is also in place to supply 2.2 MMTPA LNG from Train 4 to Sumitomo Corporation.5
Thousands of jobs have been generated during the construction phase, in addition to 200 new permanent jobs at the liquefaction plant. Freeport claims to contribute indirectly to 30,000 new jobs because of exploration and production of the feed gas supply. The company contributes to and works with various local civic and humanitarian organizations and has donated millions of dollars to support education, health, arts and sciences.6
Freeport asserts strong environmental stewardship, having given nearly 350 acres of land containing various types of habitat to conservation groups and created 35 acres of wetlands on Quintana Island.
Freeport LNG is only the second major LNG plant (Train capacity > 2 MMTPA) in the world and the first in the United States to have all-electric compressor drivers (eLNG concept) to mitigate emissions and reduce start-up time. When in operation, it is expected to be the largest electrical driven LNG plant in the world and the largest power consumer in the state of Texas.
OWNERSHIP (Equity %)
| Train 1 | |
| Freeport LNG | NA |
| Chubu Electric | NA |
| Osaka Gas | NA |
| Train 2 | |
| Freeport LNG | NA |
| IFM Investors | NA |
| Train 3 | |
| Freeport LNG | 100% |
| Train 4 | |
| Freeport LNG | 100% |
General Data
| Estimated Capital Cost (USD) | 5.65 billion (Train 1) 5.30 billion (Train 2) 4.65 billion (Train 3) TBA (Train 4) |
| Plant Type | Onshore Modular |
| Plant Stage | Under construction (Trains 1 to 3) Pre-FID / FEED (Train 4) |
| Final Investment Decision (FID) Year | 2014 (Trains 1 & 2) 2015 (Train 3) 2019 (Train 4) |
| FEED Contractor | Trains 1 to 3: McDermott Zachry Group Train 4: McDermott (CB&I) Chiyoda Corporation Zachary Group |
| EPC Contractor | Trains 1 & 2: McDermott (CB&I) Zachry Group Trains 3 & 4: McDermott (CB&I) Chiyoda Corporation Zachary Group |
| No. of Trains / capacity | 4 Trains / 4.64 MMTPA each |
| Production Start Year | 2019 (Trains 1 & 2) 2020 (Train 3) 2024 (Train 4) |
| Products | LNG, Condensate |
| Gas Type | Shale |
Technical Data
| Cooling Media | Air |
| Liquefaction Technology | APCI AP-C3MR™ |
| Refrigeration Train Details: | |
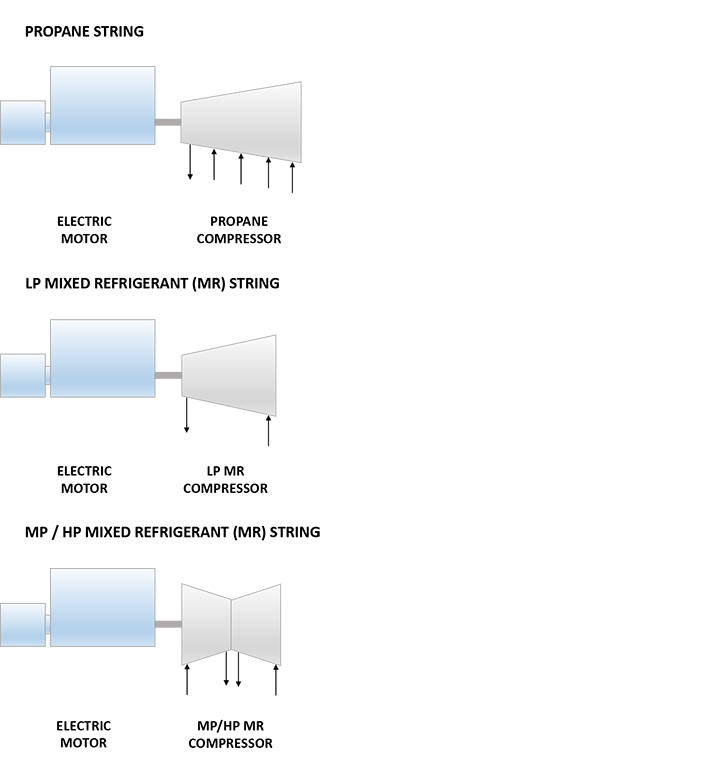
| Propane String | |
| Driver | GE Power 75 MW Synchronous Motor |
| Propane Compressor | 3MCL1605 GE (Nuovo Pignone) Horizontally Split Centrifugal Compressor |
| Low Pressure (LP) Mixed Refrigerant (MR) String | |
| Driver | GE Power 75 MW Synchronous Motor |
| LP MR Compressor | MCL1065 GE (Nuovo Pignone) Horizontally Split Centrifugal Compressor |
| Medium Pressure (MP) / High Pressure (HP) Mixed Refrigerant (MR) String | |
| Driver | GE Power 75 MW Synchronous Motor |
| MP / HP MR Compressor | 2BCL1007 GE (Nuovo Pignone) Radially Split Centrifugal Compressor |
Refrigeration Train Configuration
Key Facts
- Freeport LNG is only the second major LNG plant (Train capacity > 2 MMTPA) in the world and the first in the United States to have all-electric compressor drivers (eLNG concept). When in operation, it is expected to be the largest electrical driven LNG plant in the world.8
- Each train has three 75 MW synchronous, 2-pole motors with LCI (Load Commutated Invertor) drives for variable speed operation.9
- The motors are the largest size to be used in an LNG facility and a new motor frame was specifically designed by GE for the project.9
- The large variable speed LCI drives and LCI harmonic filters necessitated the need for several studies including inter-harmonic studies and sub-synchronous torsional interaction (SSTI) studies. The installed system will include GE’s Torsional Vibration Control System (TVCS) which is used to measure torsional vibrations from the drive train and has an active damping system for real-time control of torsional stress on the train as well as a grid damping system for damping electrical feedback into the plant power system from the drives (to prevent SSTI events).9
- Once all 3 trains are in operation, the Freeport LNG facility will become the largest power consumer in the state of Texas.10
- It is the only LNG facility where the warm end (called the pretreatment facility or PTF) and the cold end (called the liquefaction facility or LQF) are separated by a substantial distance of almost 10 miles. The LQF is located on Quintana Island while the PTF is near Stratton Ridge. One of the drivers for the separation of the PTF and LQF was to limit greenhouse gas emissions on Quintana Island.11
- In April 2018, Freeport LNG announced a 9-month delay to the project commercial start date. Trains 1-3 were originally scheduled to start production from Q4 2018 through to Q2 2019. The new production start dates were moved out to Sept. 1, 2019 for Train 1 with Trains 2 and 3 coming online in Q1 and Q2 2020. The two main reasons cited for the delay were post hurricane Harvey flooding of lay-yards where equipment, including steel piping, was stored, as well as contractor execution delays.12
- Chicago Bridge & Iron Co. (CB&I), the prime contractor of the EPC consortium building Freeport LNG was acquired by McDermott International Inc. in May 2018. CB&I’s stock had collapsed in summer 2017, with the company announcing a USD 548 million write-down in August 2017 due to cost overruns on several projects.13
- In November 2018, Toshiba Corp announced its plan to sell its US LNG business, including its Freeport LNG Contract, to Chinese gas firm ENN Energy Holdings. Toshiba is expected to post a loss of nearly $880 million from the sale.14
Source:
1. http://freeportlng.com/about/corporate-history
2. https://www.westerndredging.org/phocadownload/GulfCoast/2016Meeting/009_Hull-Jason_Johns-Michael_Port_Freeport_Infrastructure_Investment_Recent_Future_Ch_Development.pdf
3. https://www.lngworldnews.com/freeport-lngs-train-1-start-up-delayed/
4. https://www.hydrocarbons-technology.com/projects/freeport-lngs-liquefaction-texas/
5. https://www.lngworldnews.com/freeport-lng-signs-sumitomo-as-first-train-4-foundation-customer/
6. http://freeportlng.com/community-environment/community-involvement/
7. http://freeportlng.com/community-environment/environmental-stewardship/
8. https://www.businesswire.com/news/home/20140910005789/en/Freeport-LNG-Selects-GE-Major-North-American
9. http://www.gastechevent.com/sites/default/files/D2_T1_Simone%20Lazzari%20-%20Leonardo%20Baldasarre_GE%20O%26G.pdf
10. http://freeportlng.com/our-business/gas-liquefaction/
11. http://www.theislemagazine.com/construction-live.html
12. https://www.spglobal.com/platts/en/market-insights/latest-news/natural-gas/041818-freeport-lng-confirms-train-1-start-seen-in-september-2019-cites-flooding-of-yards
13. https://www.bloomberg.com/gadfly/articles/2017-12-19/mcdermott-cb-i-deal-cheap-for-a-reason
14. https://www.reuters.com/article/toshiba-outlook-lng-sale/toshiba-to-sell-u-s-lng-business-to-chinas-enn-energy-holdings-media-idUST9N1WK067






















































