In 1971, natural gas was discovered in the North Field, which is spread over a 6000 square kilometre area off the northeast coast of Qatar. The importance of this monumental discovery took a long time to percolate into commercial gain. Multiple drilling appraisals over 15 years confirmed that the field was the largest non-associated natural gas field in the world, home to almost 10% of the world’s known reserves. Suddenly Qatar found itself as owner of the third largest gas reserves in the world, after Russia and Iran. The North Field Bravo off-shore complex (NFB) was commissioned in 1996 and the RasGas Alpha off-shore complex (RGA) was started in 1999. The off-shore operations now comprise of 209 wells, which supply 18.5 billion cubic feet of sour gas daily.
In the mid-1990s Qatar invested millions of dollars to develop the port facilities and associated infrastructure at Ras Laffan, to facilitate the exploration, storage and export of its massive natural gas resources. The location, 80 kms north-east of Doha, was in ideal proximity to the North Field, as well as advantageously positioned on international maritime routes to the Far East and Europe. The on-shore operations at Ras Laffan Industrial City are spread over 7.80 square kilometres. By 2005 the port had shipped over 1000 cargos and by 2015 this number rose rapidly to 5000.
The history of LNG in Qatar started with the establishment of Qatar Liquefied Gas Company Limited (Qatargas 1) in 1984. In 1996, Qatar received delivery of its first LNG Vessel – “Al-Zubara”. Initially the operations proceeded at a glacial pace, with eight years underway before the first Sale and Purchase Agreement (SPA) was signed and 12 years for delivery of first LNG cargo. However, by 2010, Qatar established itself as the largest producer of LNG in the world with a capacity to export 77 MMTPA of LNG.
Qatar Petroleum (65%), ExxonMobil (10%), Total (10%), Mitsui (7.5%), and Marubeni (7.5%) owned Qatargas 1 project consists of 3 LNG Trains. In 1992, Qatar’s first LNG Sale Purchase Agreement (SPA) was signed with Chubu Electric of Japan for supply of 4 MMTPA of LNG. This was further backed by another SPA with 7 other Japanese buyers for supply of 2 MMTPA for 25 years. The foundation stone for the project was laid in 1994 and in October 1995 the project was in peak construction with a manpower build-up of over 9000 personnel.
In 1996, Qatar produced its first LNG and shipped its first LNG cargo to Japan. The Qatargas 1 project was officially inaugurated in 1997. 1,600 million standard cubic feet (45 million cubic metres) of raw natural gas is supplied to the plant daily from 20 production wells. In 2005 the production capacity of the project was successfully increased to almost 10 MMTPA through an efficient debottlenecking process. In 2008, Qatar received delivery of the first Q-flex vessel “Mozah”. Today the country has a fleet of 41 Q-Flex and Q-Max vessels, which are the largest LNG carrying capacity vessels in the world.
In 2018, Qatargas and RasGas operations were merged into one global energy operator – Qatargas. Today the Ras Laffan Industrial City (RLIC) is home to a workforce of approximately 115,000 personnel. Qatargas is working towards Qatarization of its workforce and aims to accomplish over 50% Qatari workers by 2030. There is a strong focus on hiring, training and maintaining Qatari employees. Qatar Petroleum together with US University Texas A&M established, the Ras Laffan Emergency and Safety College for imparting training on industrial, hazardous materials, municipal, rescue and emergency medical services. In line with the goals of Qatar National Vision (QNV) 2030, Qatargas not only strives to exceed regulatory requirements, but also proactively works on initiatives for Green House Gas (GHG) management, sustainable waste management and waste reduction, wastewater management, air emission control and flare reduction. In 2015, the Jetty Boil-off Gas Recovery project (JBOG) was inaugurated in order to mitigate the flaring at Ras Laffan LNG loading berths by 90%.
OWNERSHIP (Equity %)
| Qatar Petroleum | 65.00% |
| Total Fina Elf | 10.00% |
| ExxonMobil | 10.00% |
| Marubeni | 7.50% |
| Mitsui | 7.50% |
General Data
| Estimated Capital Cost (USD) | 2.3 B |
| Plant Type | Onshore Stick-built |
| Plant Stage | Operating |
| Final Investment Decision (FID) Year | 1992 |
| FEED Contractor | M.W. Kellogg Company (now, KBR) |
| EPC Contractor | Chiyoda Corporation |
| No. of Trains / capacity | 3 Trains / 3.2 MMTPA each |
| Production Start Year | 1996 (Train 1) 1997 (Train 2) 1998 (Train 3) |
| Products | LNG, LPG, Condensate, Sulphur, Helium |
| Gas Type | Non-associated Gas (NAG) |
Technical Data
| Cooling Media | Seawater |
| Liquefaction Technology | APCI AP-C3MR™ |
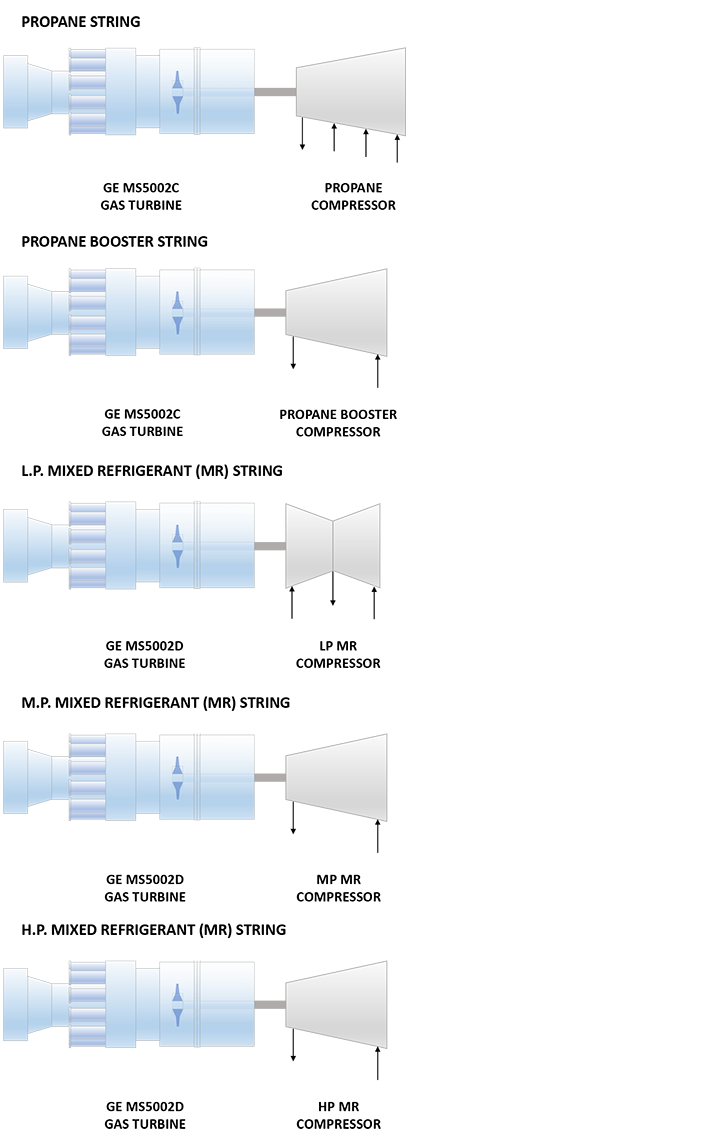
| Refrigeration Train Details: | |
| Propane String | |
| Driver | GE MS53382C (Frame 5C) Heavy Duty Gas Turbine |
| Propane Compressor | 3MCL1003 GE (Nuovo Pignone) Horizontally Split Centrifugal Compressor |
| Propane Booster String | |
| Driver | GE MS53382C (Frame 5C) Heavy Duty Gas Turbine |
| HP Propane Compressor | GE (Nuovo Pignone) Centrifugal Compressor |
| Low Pressure (LP) Mixed Refrigerant (MR) String | |
| Driver | GE MS5432D (Frame 5D) Heavy Duty Gas Turbine(Upgraded from GE MS53382C) |
| LP MR Compressor | DMCL1006 GE (Nuovo Pignone) Horizontally Split Centrifugal Compressor |
| Starter/Helper | |
| Medium Pressure (MP) MR String | |
| Driver | GE MS5432D (Frame 5D) Heavy Duty Gas Turbine(Upgraded from GE MS53382C) |
| MP MR Compressor | MCL1003 GE (Nuovo Pignone) Horizontally Split Centrifugal Compressor |
| High Pressure (HP) MR String | |
| Driver | GE MS5432D (Frame 5D) Heavy Duty Gas Turbine(Upgraded from GE MS53382C) |
| HP MR Compressor | BCL804 GE (Nuovo Pignone) Radially Split Centrifugal Compressor |
| Power Generation | 6 x GE PG6581B DLN1 (Frame 6B) Heavy Duty Gas Turbines |
Refrigeration Train Configuration
Key Facts
- Qatargas 1 (QG1) is the first grass roots LNG project in Qatar. The plant uses APCI’s Propane Precooled MR process and is designed to run for 30 years in the hot and salt-rich ambient conditions. Feed gas is transported to the facility over 80 km via a single 32 inch subsea pipeline. The first two trains were completed one month ahead of schedule. Excluding scheduled shut-downs, the plant targets achieving 95% availability. 1,2
- The project signed its first SPA in May 1992 with Japan’s Chubu Electric for a period of 25 years, and has been delivering LNG to the Japanese customer since January 1997.1
- A few months after start-up, train 1 experienced Sulphinol unit foaming, which required the plant capacity to be reduced. Several countermeasures were employed and since August 1997, the plant has not encountered any load change on this account. 1
- In 2001, process optimizations were implemented at Qatargas 1 to increase the capacity from 6 MMTPA to 7 MMTPA. The optimizations included increasing the MR discharge pressure, modifying the MR composition, decreasing propane suction pressure, modifying the nitrogen column trays to avoid LNG carryover with the end flash gas, and modifying the mercury removal beds to stop carbon fines carryover to the Sulfinol Absorber to reduce foaming. Capacity could not be increased further due to contractual environmental limitations on Sulphur emissions.3
- In 2002, the Sulphur Recovery Expansion project (SRX) was implemented. As a result the project exhibited a drastic reduction in Sulphur emissions to below legal environmental requirements. Consequently the LNG production increased by 10% to 7.7 MMTPA.3
- A Debottlenecking Project (DBN) costing approximately $185 million was executed at Qatargas between 2003 and 2005. As a result the plant capacity was upgraded to 9.5 MMTPA. This included: 3
> Upgrade of the MR Gas Turbine from a Frame 5C to Frame 5D
> Upgrade of MR Compressors (new internals)
> Replacement of the Main Propane Compressors with larger capacity units
> Replacement of the Booster Compressors & motors with larger capacity compressors driven by GE Frame 5C Gas Turbines
> Replacement of the MR LP Propane Evaporators with larger units
> Replacement of the LNG pumps internals
> Modification of the Fuel Gas System to improve the quality of fuel (Wobbe Index) feeding the process gas turbines
> Addition of a new Boil-Off Gas Compressor - Qatargas was the first company in Qatar to establish an ambient air quality program, which set a benchmark for all future air emissions control programs at Ras Laffan.4
- In 2011, Qatargas signed a contract with GE Oil & Gas to upgrade the existing Frame 6B gas turbine generators with DLN1 combustion technology to reduce NOx emissions. The upgrades were executed in 2012-13.4
- Qatargas partnered with GE, to perform the first modular change-out of a heavy-duty industrial engine at an LNG plant. At the time, modular change-outs had been performed only for aero-derivative engines, while ‘standard’ in-situ overhaul was a norm for such operations. The modular approach cut-down the major overhaul turnaround time from an average of 634 hours to an average of 428.5
- A fleet of seven 135,000 m3 capacity LNG carriers are employed to transport 4 MMTPA from Train 1 & 2 and an additional three carriers are assigned to Train 3. ‘Al Zubarah’, Qatargas’ first LNG carrier, carried the project’s maiden shipment on 23 December 1996.6
- In 2010, a plateau maintenance project (PMP) was carried out by increasing the feed gas rates from offshore wells and constructing a new acid gas removal and Sulphur recovery unit near the existing units.7
- In 2013, Continuous emission monitoring solution (CEMS) units were installed over the gas and Sulphur recovery incinerator exhaust stacks to reduce the Sulphur level in the feed gas.7
Source:
1. Rahman A.R.A. et al. ‘First LNG from Giant North Field: Qatar Gas LNG’, 12thInternational conference on Liquefied Natural Gas, Perth, Australia, May 1998
2. ‘Qatar Petroleum – Annual Report 2014’, Qatar Petroleum Website, 2014
3. Haouari A. et al ‘Qatargas Success Story‘, Gastech 2005, March 2005
4. ‘Qatargas picks GE combustion technology’, Trade Arabia Website, 5 December 2011
5. Cinelli F. et al ‘New solutions for the improvement of turbocompressor availability‘, GE Oil & Gas, 2009
6. ‘30 Years: The Qatargas Journey’, The Pioneer Magazine, 30th Anniversary Special Edition, 2015
7. ‘Qatargas I LNG Plant, Ras Laffan, Qatar’, Hydrocarbons Technology Website






















































