In 1963 large gas reserves were discovered at the South West Ampa gas field off Brunei Coast. To monetize these reserves Brunei had to overcome major challenges such as long distances to potential markets, an unproven gas liquefaction technology and inexperience in LNG shipping. In December 1969, Brunei LNG Limited was established, leading to signing of a JV agreement between the Government of Brunei, Shell Overseas Holdings Limited and Mitsubishi Corporation in January 1970. Later the same year a 20-year SPA was signed between Coldgas Trading Limited and the Tokyo Electric Power Company Incorporated, Tokyo Gas Co. Ltd. and Osaka Gas Co. Ltd.1
In 1972, Brunei LNG at Lumut in Belait district of Brunei, became the first LNG plant in the Western Pacific. S.S. Gadinia, a custom-built LNG carrier, delivered the first cargo from the 130-hectare facility to the Osaka Gas Corporation terminal in Japan. In 1989 major rejuvenation was undertaken to extend the plant life, which led to the extension of the SPA with the Japanese buyers for another 20 years in 1993. In 1994, a short-term agreement was signed with South Korean customers. The second major rejuvenation project at the facility was commenced in 2004. In the 45 plus years, Brunei LNG has dispatched over 6500 cargoes totaling more than 210 million tonnes of LNG, resulting in Natural Gas becoming the major revenue earner for Brunei.2
The plant was initially supplied with gas from Brunei Shell Petroleum’s (BSP) offshore fields at South-West Ampa, Fairley and Gannet. In 1999 Total added to this supply from its Jamalul Alam and Maharaja Lela fields and in 2003 BSP introduced supply from its Egret gas field. LNG is the main product from the plant, whereas LPG is a by-product, which is bottled for domestic sale. A cogeneration plant was built in 1987 for providing reliable and cost-effective domestic power to the region. The waste heat from the power plant is harnessed to improve efficiency of the LNG plant.3
Brunei LNG boasts of employing more than 600 people and contributing to several educational, religious and social activities, which includes the handing over of the Liang Lumut Recreational Club’ (LLRC) for recreational, sports, educational and religious events to the local community. The management is committed to complying with the most stringent environmental standards. Their ISO 14001 certified Environmental Management System is aimed to minimize emissions & flaring, reduce usage of fresh water & energy, avoid spills & leaks and conserve biodiversity.4
OWNERSHIP (Equity %)
| Government of Brunei | 35.50% |
| Shell Overseas Holdings Limited | 25.00% |
| Mitsubishi Corporation | 25.00% |
General Data
| Estimated Capital Cost (USD) | Not Available |
| Plant Type | Onshore |
| Plant Stage | Operating |
| Final Investment Decision (FID) Year | 1970 |
| FEED Contractor | WorleyParsons |
| EPC Contractor | WorleyParsons JGC Corporation |
| No. of Trains / capacity | 5 Trains / 1.44 MMTPA each |
| Production Start Year | 1972 (Train 1) 1973 (Train 2, 3, 4) 1974 (Train 5) |
| Products | Propane, LPG, Condensate |
| Gas Type | Associated Gas |
Technical Data
| Cooling Media | Seawater |
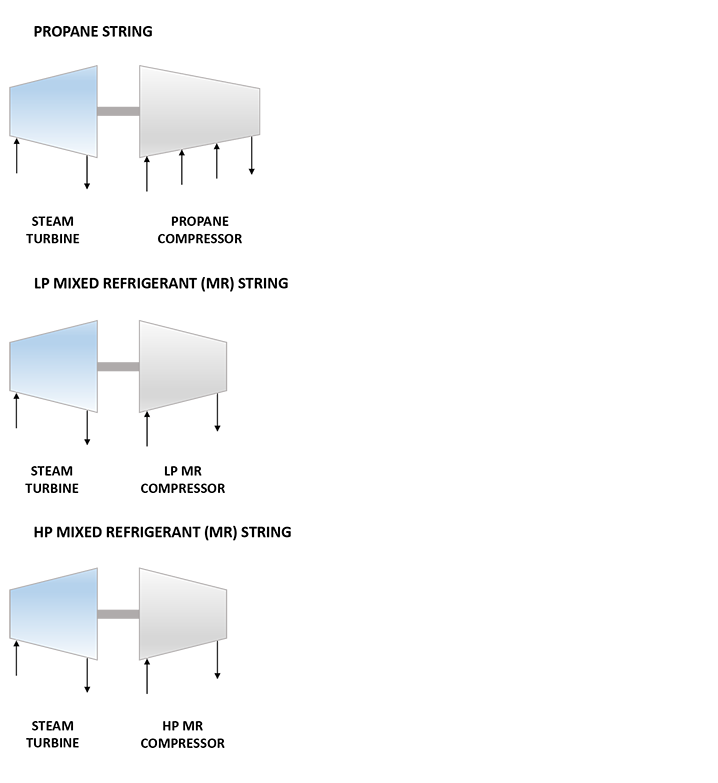
| Liquefaction Technology | APCI AP-C3MR™ |
| Refrigeration Train Details: | |
| Propane String | |
| Driver | Mitsubishi 9CL-11 Steam Turbine |
| Propane Compressor | Mitsubishi Compressor Corporation Horizontally Split Centrifugal Compressor |
| Low Pressure (LP) Mixed Refrigerant (MR) String | |
| Driver | Mitsubishi 9CL-11 Steam Turbine |
| LP MR Compressor | Mitsubishi Compressor Corporation Horizontally Split Centrifugal Compressor |
| HP Mixed Refrigerant (MR) String | |
| Driver | Mitsubishi 9CL-11 Steam Turbine |
| HP MR Compressor | Mitsubishi Compressor Corporation Radially Split Centrifugal Compressor |
| Power Generation | Steam Turbine Generators |
Refrigeration Train Configuration
Key Facts
- Brunei LNG employed the first application of APCI’s C3MR® liquefaction process. It was only the second LNG plant with APCI’s spool-wound aluminum heat exchangers and the first to go with a larger 2-bundle design.
- Brunei LNG was the first LNG plant with refrigeration compressors and steam turbines supplied by Mitsubishi.
- Originally, the Brunei LNG project included 4 trains with a design capacity of 1.05 MMTPA each. During the construction phase of the project, the scope was increased to 5 trains. As the main cryogenic heat exchanger (MCHE) of the 5th train was produced later, an updated design was installed in Train 5.5
- Between 1989-1994, major rejuvenation work was performed to extend plant life.1
- In 2004, Brunei LNG embarked on a second major plant rejuvenation project. The work scope included replacing four out of five MCHEs. The new MCHEs were designed to equal the maximum capacity of the existing units plus design margin.
- The rejuvenation project also included other major work scopes including rejuvenation of the power plant and the cooling water system. The full scope of the rejuvenation project was completed in 2010.4
- Some interesting and significant milestones achieved by Brunei LNG are as follows:2
> In 2004, Brunei LNG became the first LNG plant to be awarded with ISO 14001.
> From 2008-2010, it was ranked 1st in the Global LNG bench-marking exercise on several parameters including safety, plant availability, reliability and cost.
> 2012, Brunei LNG celebrated 40 years of successful delivery of LNG cargoes to Japan and in June 2015, it achieved its 6500th cargo delivery to Japan.
> In 2012, Brunei LNG became the first LNG plant worldwide to overhaul the loading arms.
> By October 2013, it achieved 22 Million man-hours without a Lost Time Incident (LTI). - The energy consumption of the plant is the equivalent of a 300 MW power station, enough to supply the whole of Brunei Darussalam. It incorporates nine steam boilers which drive the turbine compressors and turbine generators.3
- 2000 cubic meters per hour of water is being used to cool refrigerant streams, to make drinking water and to feed the steam boilers. This comes from the Badas River via three 16-kilometer pipelines and is treated and re-circulated.3
Source:
1. Brunei LNG History and Background
2. Brunei LNG Milestones
3. Brunei LNG – The Plant
4. Brunei LNG Corporate Social Responsibilities
5. Omarali A. et al ‘Main Cryogenic Heat Exchanger Replacement at Brunei LNG’, IPTC, 2005






















































