In 1971, natural gas was discovered in the North Field, which is spread over a 6000 square kilometre area off the northeast coast of Qatar. The importance of this monumental discovery took a long time to percolate into commercial gain. Multiple drilling appraisals over 15 years confirmed that the field was the largest non-associated natural gas field in the world, home to almost 10% of the world’s known reserves. Suddenly Qatar found itself as owner of the third largest gas reserves in the world, after Russia and Iran. The North Field Bravo off-shore complex (NFB) was commissioned in 1996 and the RasGas Alpha off-shore complex (RGA) was started in 1999. The off-shore operations now comprise of 209 wells, which supply 18.5 billion cubic feet of sour gas daily.
In the mid-1990s Qatar invested millions of dollars to develop the port facilities and associated infrastructure at Ras Laffan, to facilitate the exploration, storage and export of its massive natural gas resources. The location, 80 kms north-east of Doha, was in ideal proximity to the North Field, as well as advantageously positioned on international maritime routes to the Far East and Europe. The on-shore operations at Ras Laffan Industrial City are spread over 7.80 square kilometres. By 2005 the port had shipped over 1000 cargos and by 2015 this number rose rapidly to 5000.
The history of LNG in Qatar started with the establishment of Qatar Liquefied Gas Company Limited (Qatargas 1) in 1984. In 1996, Qatar received delivery of its first LNG Vessel – “Al-Zubara”. Initially the operations proceeded at a glacial pace, with eight years underway before the first Sale and Purchase Agreement (SPA) was signed and 12 years for delivery of first LNG cargo. However, by 2010, Qatar established itself as the largest producer of LNG in the world with a capacity to export 77 MMTPA of LNG.
In 1999, the RasGas 1 project started operations at a facility south of the existing Qatargas plant. In 2001, Ras Laffan Liquefied Natural Gas Company Limited 2 (RL2) was founded to construct 3 new LNG trains of capacity 4.7 MMTPA each. The very same year the company signed an agreement with Edison Gas for supplying 3.5 MMTPA LNG for 25 year starting 2005. The foundation stone for RasGas train 3 was laid in 2002. Heads of Agreement were signed in 2003 with ExxonMobil for LNG exports to USA and in 2005, RL2 agreed to supply 3 MMTPA of LNG to CPC Corporation of Taiwan.
The first cargo from train 3 was shipped to India in February 2004, while trains 4 and 5 were officially inaugurated in 2005 and 2006 respectively. The 2 trains receive supply from 9 bore wells and produce gas condensate, Liquefied petroleum gas (LPG), butane and propane in addition to the LNG.
RasGas 2 boast of several technological firsts. Train 4 was the first LNG train to operate an acid-gas reinjection scheme, that stores Carbon Dioxide and Hydrogen Sulphide and reinjects CO2 into a saline aquifer. Train 3 was able to become one of the most optimized LNG trains ever built, using helper motors to boost performance of turbo-compressors, reconfigured refrigerant compressors, new gas-treating technology and the use of a hydraulic turbine. The off-shore facilities for train 3 eliminated the need for process platforms, by switching from a dry-gas (gas and condensate) to a wet-gas (gas, condensate and water) scheme.
In 2018, Qatargas and RasGas operations were merged into one global energy operator – Qatargas. Today the Ras Laffan Industrial City (RLIC) is home to a workforce of approximately 115,000 personnel. Qatargas is working towards Qatarization of its workforce and aims to accomplish over 50% Qatari workers by 2030. There is a strong focus on hiring, training and maintaining Qatari employees. Qatar Petroleum together with US University Texas A&M established, the Ras Laffan Emergency and Safety College for imparting training on industrial, hazardous materials, municipal, rescue and emergency medical services. In line with the goals of Qatar National Vision (QNV) 2030, Qatargas not only strives to exceed regulatory requirements, but also proactively works on initiatives for Green House Gas (GHG) management, sustainable waste management and waste reduction, wastewater management, air emission control and flare reduction. In 2015, the Jetty Boil-off Gas Recovery project (JBOG) was inaugurated in order to mitigate the flaring at Ras Laffan LNG loading berths by 90%.
OWNERSHIP (Equity %)
| Qatar Petroleum | 70.00% |
| ExxonMobil | 30.00% |
General Data
| Estimated Capital Cost (USD) | 1.67 B per Train |
| Plant Type | Onshore Stick-built |
| Plant Stage | Operating |
| Final Investment Decision (FID) Year | 2000 |
| FEED Contractor | Chiyoda Corporation |
| EPC Contractor | Chiyoda Corporation Snamprogetti |
| No. of Trains / capacity | 3 Trains / 4.7 MMTPA each |
| Production Start Year | 2004 (Train 3) 2005 (Train 4) 2007 (Train 5) |
| Products | LNG, LPG, Condensate |
| Gas Type | Non-associated Gas (NAG) |
Technical Data
| Cooling Media | Seawater |
| Liquefaction Technology | APCI AP-C3MR/SplitMR® First ever application |
| Refrigeration Train Details: | |
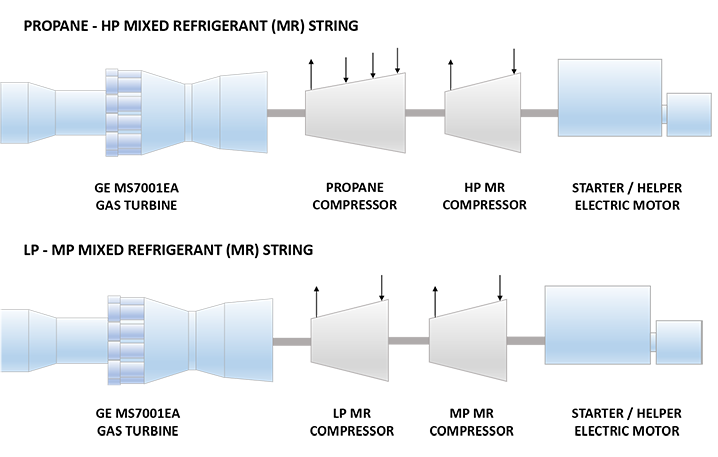
| Propane – HP Mixed Refrigerant (MR) String | |
| Driver | GE MS7121EA DLN1 (Frame 7EA) Heavy Duty Gas Turbine |
| Propane Compressor | 88M8-5 Elliott Horizontally Split Centrifugal Compressor |
| High Pressure (HP) MR Compressor | 56MB5 Elliott Radially Split Centrifugal Compressor |
| Starter/Helper Motor | ABB 12 MW Synchronous Motor with LCI Drive |
| LP – MP Mixed Refrigerant (MR) String | |
| Driver | GE MS7121EA DLN1 (Frame 7EA) Heavy Duty Gas Turbine |
| Low Pressure (LP) Compressor | 88M4 Elliott Horizontally Split Centrifugal Compressor |
| Medium Pressure (MP) MR Compressor | 60M4 Elliott Horizontally Split Centrifugal Compressor |
| Starter/Helper Motor | ABB 12 MW Synchronous Motor with LCI Drive |
Refrigeration Train Configuration
Key Facts
- RasGas 2’s key customers are Petronet LNG of India for Train 3; Edison for Train 4; and CPC Corporation of Taiwan, ENI of Italy and EDF Trading of France for Train 5. These customers have signed long term SPAs of over 20 years. India and Taiwan purchase LNG on FOB-basis (Free-on-Board) while the others buy on DES-basis (Delivered Ex Ship).1
- RasGas 2’s Train 3 is capable of processing rich LNG, while Trains 4 & 5 can process both rich and lean LNG.2
- RasGas 2 (RG 2) trains employ the APCI propane, mixed refrigerant design. Each refrigeration compressor string is driven by a GE Frame 7EA gas turbine and an ABB starter/helper electric motor. The plant faced seasonal reduction in LNG production, of approximately 5% from March to August, due to reduced gas turbine power and greater cooling water temperature. A $150 million optimization initiative was undertaken to address this seasonal impact. The project spanned over 42 months and resulted in approximately 20 shutdown-days for retrofitting the propane compressor.2
- RasGas together with Qatargas operate the $1 Billion Jetty Boil-off Gas Recovery (JBOG) Project in Ras Laffan Industrial City. The JBOG project, touted as the biggest environmental project in the world, is designed to eliminate flaring by 90%. Annually, approximately 29 million cubic feet of natural gas, which was previously flared during LNG ship loading, is recovered and utilized in the LNG plants as feed or fuel. This is equivalent to saving 1.6 million tonnes of CO2 per year.3
- RasGas 2 Train 3 was the first train in the world to employ two identical Frame 7E drivers, to implement a novel compressor-driver arrangement comprising both propane and mixed-refrigerant (MR) compressors on a single shaft. This arrangement not only offered better efficiency and economies of scale, but also eased the procurement, maintainability, and sparing operations, through the use of same type and model of gas turbine driver across services. Trains 4 and 5 subsequently started up employing the same concept. 12 MW electric motors are used for starting, however the selected motors are rated for continuous use and coupled with individual VFD to supplement GT power during the hot summer months. The effectiveness of this arrangement in many ways contributes to the additional annual processing capacity of RasGas 2 trains over RasGas 1 trains.4
- On 27 August 2012, RasGas was hit by an unknown virus which required shutting down of the company’s website and email servers. However, this attack did not impact operations, production and cargo deliveries. The event followed a malware attack against Saudi Aramco on 15 August 2012 which forced the world’s largest oil company to take down its company-wide office systems for twelve days.5
- RasGas entered the LNG market claiming one of the lowest cost-per-ton of LNG produced in the industry. RasGas 1 & 2 (RG1 and RG2) were the world’s first LNG plants to use GE Frame 7 driven Propane MR compressor.6
Source:
1. ‘The LNG industry GIIGNL Annual Report 2018’, GIIGNL Website, 2018
2. Dr. White N., Master D. ‘Mitigation of Seasonal Production Loss for Three Parallel 4.7 MMTPA LNG Trains’, 17th International Conference & Exhibition on Liquefied Natural Gas (LNG 17), Houston, USA, April 2013
3. ‘Qatar Petroleum Annual Report 2014’, Qatar Petroleum Website, 2014
4. Brimm A. et al. ‘Operating Experience with the Split MR Machinery Configuration of the C3MR LNG Process’, Society of Petroleum Engineers – Project Facilities and Construction, June 2006
5. Zetter K. ‘https://www.wired.com/2012/08/hack-attack-strikes-rasgas/’, Wired Website, 30 August 2012
6. Dr. Akhtar S. ‘Driver Selection for LNG Compressors’, MSE Consultants Website, 14 December 2004






















































