The establishment of Woodside (Lakes Entrance) Oil Co NL in 1954, followed by the permission to explore 370,000 square kilometres off Western Australian coast in 1963 and the formation of the North West Shelf Venture, are not only significant milestones in the history of the Karratha Gas Plant but also in the history of LNG in Australia. In 1968, Woodside first found oil in the NW Shelf, followed by major gas and condensate discoveries in 1971. In 1980, construction of an onshore gas plant was commenced in Burrup Peninsula, which at that time was the largest single non-government project ever undertaken in Australian history. The Karratha Gas Plant was built approximately 1260 kilometres north of Perth.
The signing of sales agreements with 8 Japanese gas and power companies in 1985 opened the way for construction of an LNG plant, which initially housed 2 LNG trains of capacity 2.2 MMTPA each. Production started in 1989 and in 1992 the trains were modified to enhance their capacity to 2.5 MMTPA per train. The very same year, train 3 came on stream with a similar production capacity. Major expansion plans were initiated in the year 2000, backed by signing of letters of intent with the Japanese buyers. In 2002, a 25-year contract was signed with China for the supply of LNG from the plant. The facility added 4.4 MMTPA capacity in 2004, when train 4 commenced production. In April 2007, Woodside initiated phase V expansion at Karratha, which involved the construction of train 5 and associated infrastructure upgrades at the facility. The A$2.6 billion investment concluded with train 5 adding another 4.4 MMTPA capacity in 2008.
In the last 30 years the North West Shelf project has shipped over 5000 cargos. The project, which is spread over 200 hectares, is not only one of the largest in the country, but also delivers a third of Australia’s oil and gas production. It is one of the most advanced, integrated gas production systems in the world, with 5 LNG trains, 2 domestic gas trains, 6 condensate stabilization units and 3 LPG fractionation units. Gas is supplied from several fields including Goodwyn, Waneae, Rankin, North Lambert, Hermes and Cossack and also tiebacks from Echo-Yodel and Perseus. Two 130km trunk lines transport gas to the facility.
Woodside aims to contribute significantly to the local community and funds initiatives in 3 categories – philanthropy, strategic shared value partnerships and driving collective impact. Through employee volunteering & participation programs, collaboration with the community and working with government and industry, the company continues to forge stronger ties with the community. The facility employs a staff of 430 personnel and is committed to providing full, fair and reasonable opportunities to the indigenous community. Woodside claims to direct 80% of its overall spending to Australian businesses and in 2017 witnessed a 34% increase in new contracts awarded to indigenous businesses.
The company actively funds and works with scientific studies and research programs to deepen the understanding of the regional environment and how it is affected by human impact. The program with the Australian Institute of Marine Science at Scott Reef, is one of the longest and most comprehensive investigations of a reef system in the world. For three years in a row (2015, 2016 and 2017) Woodside has received the Australian Petroleum Production & Exploration Association environment excellence award. In 2018, the Dow Jones sustainability index ranked Woodside in the top 7% companies in its sector.
OWNERSHIP (Equity %)
| Woodside Energy | 16.67% |
| BHP Billiton | 16.67% |
| BP Developments Australia | 16.67% |
| Chevron Australia | 16.67% |
| Japan Australia LNG (Mitsubishi Mitsui) | 16.67% |
| Shell Development (Australia) | 16.67% |
General Data
| Estimated Capital Cost (USD) | 2.4 B Per Train |
| Plant Type | Onshore Stick-built |
| Plant Stage | Operating |
| Final Investment Decision (FID) Year | 2001 (Train 4) 2005 (Train 5) |
| FEED Contractor | Train 4: M. W. Kellogg Limited (KBR Inc.) Hatch Clough Engineering JGC Corporation Train 5: Foster Wheeler |
| EPC Contractor | Train 4: M. W. Kellogg Limited (KBR Inc.) Hatch Clough Engineering JGC Corporation Train 5: Foster Wheeler WorleyParsons |
| No. of Trains / capacity | 2 Trains / 4.6 MMTPA each |
| Production Start Year | 2004 (Train 4) 2008(Train 5) |
| Products | LNG, LPG, Condensate, Domestic Gas, Oil |
| Gas Type | Non-associated Gas (NAG) |
Technical Data
| Cooling Media | Air |
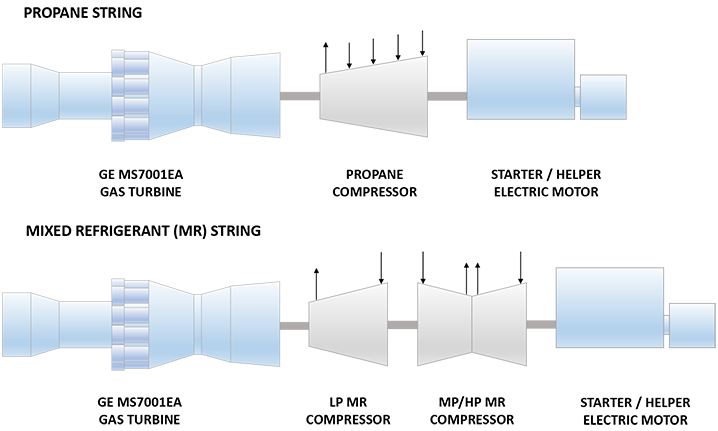
| Liquefaction Technology | Shell Propane precooled / Mixed Refrigerant (C3/MR) |
| Refrigeration Train Details: | |
| Propane String | |
| Driver | GE MS7121EA DLN1 (Frame 7EA) Heavy Duty Gas Turbine |
| Propane Compressor | 3MCL1405 GE (Nuovo Pignone) Horizontally Split Centrifugal Compressor |
| Starter/Helper Motor | 20 MW Synchronous Motor |
| Mixed Refrigerant (MR) String | |
| Driver | GE MS7121EA DLN1 (Frame 7EA) Heavy Duty Gas Turbine |
| Low Pressure (LP) MR Compressor | AN200 GE (Nuovo Pignone) Axial Compressor |
| Medium Pressure (MP) / High Pressure (HP) MR Compressor | 2BCL806 GE (Nuovo Pignone) Radially Split Centrifugal Compressor |
| Starter/Helper Motor | 20 MW Synchronous Motor |
| Power Generation | Qty: 4 GE LM6000 PD Aeroderivative Gas Turbines |
Refrigeration Train Configuration
Key Facts
- In 2018, Australia’s trade practices watchdog – Australian Competition and Consumer Commission (ACCC), conditionally allowed 6 LNG projects of Western Australia to coordinate their maintenance activities with each other, to avoid concurrent scheduled outages and to maximize efficiencies. The plants include North West Shelf, Gorgon, Wheatstone, Pluto, Prelude and Ichthys. As an added measure to eliminate undue advantage in the wholesale gas markets, ACCC required the plants to “publicly disclose maintenance schedule information that they share with each other”. The operators of these LNG plants had requested for a 10-year permission, however ACCC authorised this facility for only 5 years.1
- On November 6 2018, North West Shelf joint venture agreed to process third-party gas of Browse joint venture at the Karratha plant. The transition to a third-party tolling facility is a bid to increase the life of the Karratha gas and LNG plant beyond the end of life of the NWS Joint Venture fields and to continue operations for decades after 2025.2
- NWS Project’s Train 5 was the first onshore LNG processing train in the world to be designed & constructed in a modular form. A “Smart Clone” concept was employed to divide the stick-built Train 4’s design and replicate it into 75 individual components, which were then pre-assembled in separate locations concurrently. This approach not only allowed efficiency through parallel processing, but also enabled outsourcing of work to areas with abundant, cost effective labour. The 75 modules, weighing a consolidated 18,000 tonnes, were delivered to the site in 17 shipments, the largest shipment weighing 2,400 tonnes.3,4
- Karratha Gas Plant has reported multiple production outages, including shutdowns in January 2008, March 2009, May 2015, January 2016, April 2017, June 2017 and November 2017. Several of these incidents have been attributed to electrical faults in the plant.5,6,7,8,9,10
- In a bid to reduce costs and enhance production and reliability, Woodside Energy has initiated several innovation programs, which include the deployment of data analytics, cognitive computing, artificial intelligence (AI) and even 3D printing.
The Maximum Possible Production (MPP) tool was developed for Pluto LNG, to assist technicians in interpreting performance against benchmarked historical data. This was later put into trial at the NWS plant as well.
In 2016, Woodside deployed the IBM’s Watson cognitive computing system across its entire organization.
Woodside has also developed their own cognitive adviser tool – “Willow”, to deliver collective knowledge from the company’s operational experience to its employees to enable faster, data-driven decision making.11 - A fleet of seven vessels, owned by the North West Shelf Shipping Services Company (NWSSSC), is deployed on the Australia-Asia LNG trade route. The twin boiler and steam turbine, that drive the four-bladed propeller, can be fed by fuel oil, boil-off gas or a combination of the two. The six identical 272m long & 47m wide ships have four spherical cargo tanks, capable of holding 126,000m3 of LNG. While the 287m long & 43.4m Northwest Swan, is the newest addition to the fleet and can carry a cargo of 137,700m3.12
Source:
1. ‘LNG firms can share maintenance info’, SBS News Website, 2 March 2018
2. ‘NWS gas deals to extend life of Karratha plant’, LNG World News website, 8 November 2018
3. ‘A ‘World First’ In Modular Construction’, Foster Wheeler Website, 25 September 2008
4. Smith C., Bowtell G. ‘The First Modularisation of an LNG Plant: North West Shelf Venture Karratha Gas Plant Phase V Expansion Project’, 15th International Conference and Exhibition of Liquefied Natural Gas (LNG 15), Barcelona, Spain, April 2007
5. ‘Woodside shuts down Karratha gas plant’, The Sydney Morning Herald, 2 January 2008
6. ‘Woodside shuts down Karratha gas plant’, News.com.au Website, 17 March 2009
7. Mercer D. ‘Karratha gas plant offline’, The West Australian Website, 14 May 2015
8. Pickles S. ‘Karratha gas plant breakdown’, Business News Western Australia Website, 13 January 2016
9. Woodside resumes LNG production at Karratha gas plant’, LNG World News Website, 3 May 2017
10. ‘Woodside’s Karratha plant hit by LNG production outage’, LNG World News website, 13 November 2017
11. O’Brien J. ‘Woodside beefs up tech play’, Credit and Investments Ombudsman Australia Website, 2 March 2017
12. ‘Fleet’, NWSSSC Website






















































