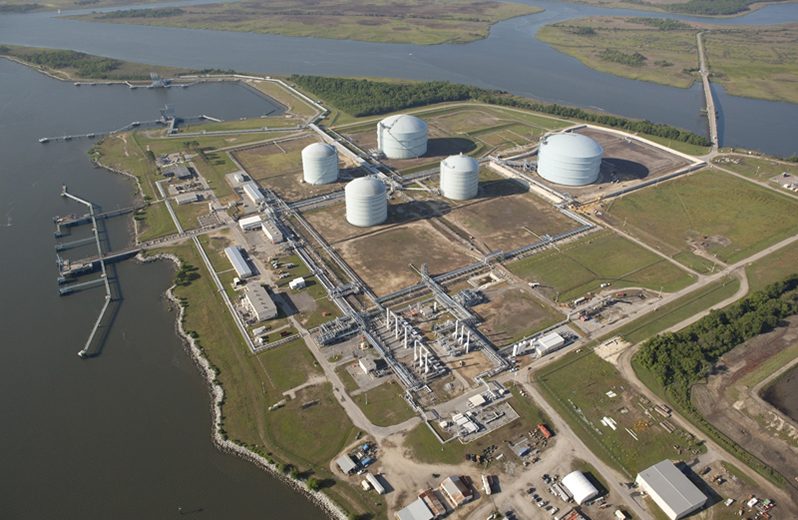
Elba Island in Chatham County, Georgia is named after an island of the same name in the Mediterranean Sea. The 840-acre private island is located near the Port of Savanna. In 1972, the Elba Island facility received initial authorization for building an LNG import and regassification terminal. The terminal was built by Sonat, Inc in September 1978, to receive gas from Algeria. However, pricing disputes led to decommissioning of the terminal in 19829. Diminishing US gas reserves triggered recommissioning and expansion of the facility in October 2001.
In June 2016, the Elba Liquefaction Project was given a go ahead by the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission (FERC), as one of many US LNG import terminals with bi-directional capabilities. The 51/49 Kinder Morgan/EIG Global Energy Partners joint venture selected a unique approach by employing multiple small units of Shell’s Moveable Modular Liquefaction System (MMLS). A total of 10 trains, each with a capacity of 0.25 MMTPA would be deployed over 2 phases, with a planned budget of US$ 2.2 billion. 6 trains are being constructed and installed in the first phase, followed by 4 in the second phase.
Shell’s MMLS units are manufactured remotely and transported to Elba Island, where they are put together. The individual modules of the plant have the flexibility to be disassembled and moved to another facility in the future if required. Marcellus Shale gas delivered via the Transco pipeline is speculated to be a source for the gas exported from the Elba Island facility.1 The first phase with 6 MMLS units was slated to be ready by mid-2018, however delays on multiple accounts including construction delays have pushed first LNG to the beginning of 2019 with the remaining trains entering operation through 2019.2 Shell has already acquired a long-term contract for 20 years, covering the full output of the Elba Island LNG plant.
The construction of the plant generated over 2,000 jobs with an average of 1,700 jobs. In addition, 100 new jobs will be created for continued operations.3 The project strategy focused on local sourcing of labor, site services and vendors for consumables, as well as working with local bodies on various issues in the interest of the community.
OWNERSHIP (Equity %)
| Kinder Morgan | 51.00% |
| EIG Global Energy Partners (EIG) | 49.00% |
General Data
| Estimated Capital Cost (USD) | 220M Per Train |
| Plant Type | Onshore |
| Plant Stage | Under construction |
| Final Investment Decision (FID) Year | 2015 |
| FEED Contractor | McDermott (CB&I) |
| EPC Contractor | IHI E&C |
| No. of Trains / capacity | 10 Trains / 0.25 MMTPA each |
| Production Start Year | 2019 (Trains 1-6) |
| Products | LNG |
| Gas Type | Shale |
Technical Data
| Cooling Media | Air |
| Liquefaction Technology | Shell Moveable Modular Liquefaction System (MMLS) |
| Refrigeration Train Details: | |
| Single-cycle Mixed Refrigerant (SCMR) String 1 & 2 | |
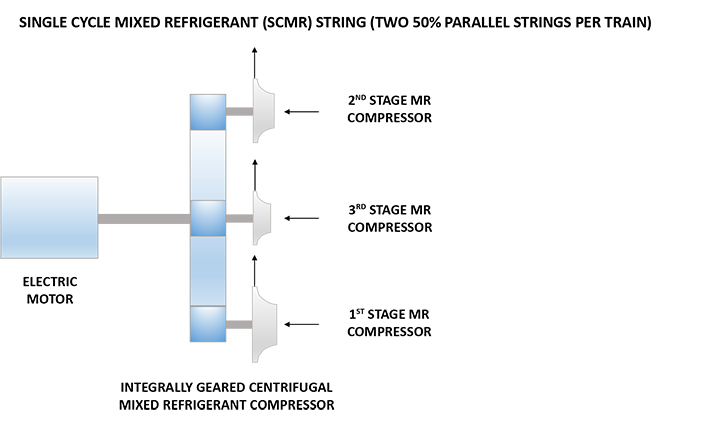
| Driver | Siemens 7.8 MW Induction Motor |
| Mixed Refrigerant Compressor | Ingersoll Rand 3-Stage Integrally Geared Centrifugal Compressor |
Refrigeration Train Configuration
Key Facts
- Elba Liquefaction Project will be the fourth export facility to come on-line in the U.S. since the recent shale gas revolution. Sabine Pass began operations in Louisiana in 2016, Cove Point LNG in Maryland began exporting in March 2018, and Corpus Christi LNG is anticipated to begin operations by the end of 2018.4
- Elba Island LNG is the largest deployment of Shell’s Moveable Modular Liquefaction System (MMLS). The liquefaction system consists a single-cycle mixed refrigerant (SCMR) composed of nitrogen, methane, ethylene, propane and isopentane. Two, parallel, 50% motor driven integrally-geared centrifugal compressors are used to compress the mixed refrigerant.5
- The MMLS units are fabricated by GE Oil & Gas. In 2013, GE Oil & Gas acquired Salof Refrigeration Inc (located in Schertz, TX, USA) which specialized in the design and fabrication of small LNG and CO2 liquefaction units.6
- Kinder Morgan inherited Elba Island after its acquisition of midstream firm El Paso in 2012.7
- Originally Shell US Gas & Power, a subsidiary of Royal Dutch Shell had 49% equity interest in Elba Island LNG. Shell sold its stake to Kinder Morgan in 2015.8
- EIG Global Energy Partners acquired their stake from Kinder Morgan in 2017.8
- Shell is committed to take 100% of the phase 1 liquefaction capacity (1.5 MMTPA) for 20 years.8
Source:
1. https://marcellusdrilling.com/2018/07/elba-island-ga-lng-startup-delayed-to-4q18/
2. https://www.lngworldnews.com/us-elba-island-lng-export-project-pushed-back-again/
3. https://www.bloomberg.com/research/stocks/news/article.asp?docKey=600-201808302245KRTRIB__BUSNEWS_26085_52578-1&ex=true&ticker=4ED:GR
4. https://www.savannahnow.com/news/20180830/elba-island-lngs-2-billion-savannah-expansion-nears-completion
5. https://www.energy.gov/sites/prod/files/2016/12/f34/EA-1963%20Elba%20Liquefaction%20FERC%20FEA%20%282016-02%29.pdf
6. https://www.genewsroom.com/press-releases/ge-agrees-to-acquire-salof-a-designer-and-manufacturer-of-small-lng-technologies-215869
7. http://www.poten.com/wp-content/uploads/2015/05/LNG_Opinion_20130821.pdf
8. https://www.kindermorgan.com/business/gas_pipelines/projects/elbaLNG
9. https://www.lngworldshipping.com/news/view,small-and-midscale-liquefaction-streamlines-lng-export-projects_51046.htm






















































