In 1971, natural gas was discovered in the North Field, which is spread over a 6000 square kilometre area off the northeast coast of Qatar. The importance of this monumental discovery took a long time to percolate into commercial gain. Multiple drilling appraisals over 15 years confirmed that the field was the largest non-associated natural gas field in the world, home to almost 10% of the world’s known reserves. Suddenly Qatar found itself as owner of the third largest gas reserves in the world, after Russia and Iran. The North Field Bravo off-shore complex (NFB) was commissioned in 1996 and the RasGas Alpha off-shore complex (RGA) was started in 1999. The off-shore operations now comprise of 209 wells, which supply 18.5 billion cubic feet of sour gas daily.
In the mid-1990s Qatar invested millions of dollars to develop the port facilities and associated infrastructure at Ras Laffan, to facilitate the exploration, storage and export of its massive natural gas resources. The location, 80 kms north-east of Doha, was in ideal proximity to the North Field, as well as advantageously positioned on international maritime routes to the Far East and Europe. The on-shore operations at Ras Laffan Industrial City are spread over 7.80 square kilometres. By 2005 the port had shipped over 1000 cargos and by 2015 this number rose rapidly to 5000.
The history of LNG in Qatar started with the establishment of Qatar Liquefied Gas Company Limited (Qatargas 1) in 1984. In 1996, Qatar received delivery of its first LNG Vessel – “Al-Zubara”. Initially the operations proceeded at a glacial pace, with eight years underway before the first Sale and Purchase Agreement (SPA) was signed and 12 years for delivery of first LNG cargo. However, by 2010, Qatar established itself as the largest producer of LNG in the world with a capacity to export 77 MMTPA of LNG.
The success of the Qatargas 1 project, with its 3 trains in operation since 1996-97, made a strong case for expanding Qatar’s gas exports. In 2002, Heads of Agreement were signed with ExxonMobil and in 2004, the Qatar Liquefied Gas Company Limited 2 (Qatargas 2) was founded. The new project involved building two mega trains each with a production capacity of 7.8 MMTPA. Train 4 is owned by Qatar Petroleum (70%) and ExxonMobil (30%), while Train 5 has Qatar Petroleum (65%), ExxonMobil (18.3%) and Total (16.7%) as shareholders.
In 2005, the foundation stone was laid to build 2 mega trains, which would make the project the world’s first fully-integrated value chain. The 2 trains, which use Air Product’s proprietary APX process technology, began production in March 2009 and September 2009. The project is backed by 30 offshore wells, three onshore injection wells for waste water disposal and 3 unmanned offshore platforms in Qatar’s North Field. 2.9 billion cubic feet of gas per day is supplied through 2 wet-gas pipelines. In addition to the 7.8 MMTPA of LNG the plant also produces 0.85 MMTPA of liquefied petroleum gas (LPG) and 90,000 barrels per day (bpd) of condensate. Qatargas 2 has at its disposal a fleet of 14 Q-Flex and Q-Max ships, which are the largest LNG carrying capacity vessels in the world.
In 2018, Qatargas and RasGas operations were merged into one global energy operator – Qatargas. Today the Ras Laffan Industrial City (RLIC) is home to a workforce of approximately 115,000 personnel. Qatargas is working towards Qatarization of its workforce and aims to accomplish over 50% Qatari workers by 2030. There is a strong focus on hiring, training and maintaining Qatari employees. Qatar Petroleum together with US University Texas A&M established, the Ras Laffan Emergency and Safety College for imparting training on industrial, hazardous materials, municipal, rescue and emergency medical services. In line with the goals of Qatar National Vision (QNV) 2030, Qatargas not only strives to exceed regulatory requirements, but also proactively works on initiatives for Green House Gas (GHG) management, sustainable waste management and waste reduction, wastewater management, air emission control and flare reduction. In 2015, the Jetty Boil-off Gas Recovery project (JBOG) was inaugurated in order to mitigate the flaring at Ras Laffan LNG loading berths by 90%.
OWNERSHIP (Equity %)
| Train 4 | |
| Qatar Petroleum | 70.00% |
| ExxonMobil | 30.00% |
| Train 5 | |
| Qatar Petroleum | 65.00% |
| ExxonMobil | 18.30% |
| Total | 16.70% |
General Data
| Estimated Capital Cost (USD) | 2.5 B per Train |
| Plant Type | Onshore Stick-built |
| Plant Stage | Operating |
| Final Investment Decision (FID) Year | 2004 |
| FEED Contractor | Chiyoda Corporation |
| EPC Contractor | Chiyoda Corporation Technip |
| No. of Trains / capacity | 2 Trains / 7.8 MMTPA each |
| Production Start Year | 2009 |
| Products | LNG, LPG, Condensate, Sulphur, Propane, Butane |
| Gas Type | Non-associated Gas (NAG) |
Technical Data
| Cooling Media | Air |
| Liquefaction Technology | APCI AP-X™ |
| Refrigeration Train Details: | |
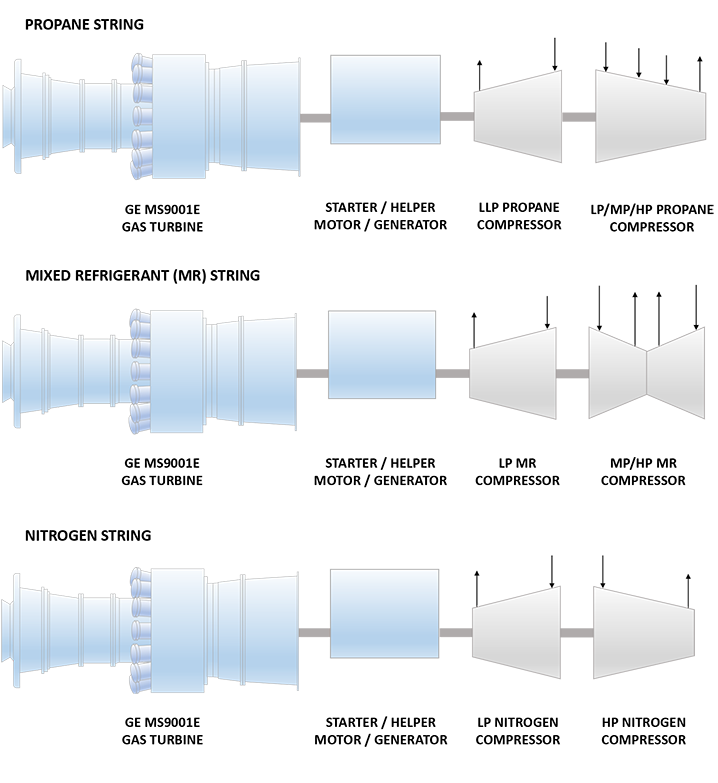
| Propane String | |
| Driver | GE PG9171E DLN (Frame 9E) Heavy Duty Gas Turbine |
| Starter Helper Motor/Generator | ASI 45 MW Synchronous Motor / Generator |
| LLP Propane Compressor | MCL1402 GE (Nuovo Pignone) Centrifugal Compressor |
| LP/MP/HP Propane Compressor | 3MCL1403 GE (Nuovo Pignone) Centrifugal Compressor |
| Mixed Refrigerant String | |
| Driver | GE PG9171E DLN (Frame 9E) Heavy Duty Gas Turbine |
| Starter Helper Motor/Generator | ASI 45 MW Synchronous Motor / Generator |
| LP MR Compressor | MCL1805 GE (Nuovo Pignone) Centrifugal Compressor |
| MP/HP MR Compressor | 2BCL1006 GE (Nuovo Pignone) Radially Split Centrifugal Compressor |
| Nitrogen String | |
| Driver | GE PG9171E DLN (Frame 9E) Heavy Duty Gas Turbine |
| Starter Helper Motor/Generator | ASI 45 MW Synchronous Motor / Generator |
| LP Nitrogen Compressor | MCL1402 GE (Nuovo Pignone) Centrifugal Compressor |
| HP Nitrogen Compressor | BCL1003 GE (Nuovo Pignone) Radially Split Centrifugal Compressor |
| Power Generation | 6 x Mitsubishi 9CL-12 (44MW) Steam Turbine Generators |
Refrigeration Train Configuration
Key Facts
- Chiyoda Corp. employed Integraph’s SmartPlant® Materials Management System to manage the EPC challenges offered by the 3 Qatari mega projects. The aim was to automate material management across all EPC processes, provide seamless interface between the materials management system and multiple 3D CAD Systems and optimize workflows to execute multiple projects concurrently.1
- On September 2007, Qatargas 2 launched four Q-Flex LNG vessels, a new class of LNG carriers, with a cargo-carrying capacity of 216,200 m3, 40% larger than the standard LNG carriers. The 315 m long vessels are propelled by two slow speed diesel engines, preferred over traditional steam turbines to achieve better fuel efficiency. The vessels also pioneer an on-board re-liquefaction system to process the boil-off gas and return the LNG back into the cargo tanks. 2,3
- In 2009, Qatargas 2 received the delivery of the first Q-Max vessel “MOZAH”, which was built by Samsung Heavy Industries. The 345 m long vessel, with a capacity of 266,000 cubic meters, is the world’s largest LNG carrier. The on-board technology is similar to the Q-flex vessels.3,4
- Qatargas 2 trains have a capacity of 7.8 MMTPA, which is almost 50% more than any other plant of the time. The plant achieved this through employing the APCI’s AP-X process technology and the first-ever use of Frame 9E gas turbines in an LNG plant. 5
- A separate motor/generator setup with variable frequency drive (VFD) is available at each Frame 9E unit to provide extra power during high ambient temperature conditions, and to “auto generate” electrical power under normal operations . Waste recovery steam generators have been used to improve overall air emissions, thermal efficiency and overall plant reliability. The systems are designed for upstream recovery of hydrocarbons whenever practical and the new flares are designed to operate as smokeless flares.5
- Qatargas 2 construction required a complete design overhaul of the acid gas removal unit, the Sulphur recovery unit, associated utilities and a plot plan. The construction phase involved 66.5 million labor man-hours, 182,600 m³ concrete pour, 9300 t steel, 28000 t pipeline and 32000 t installed equipment.6
- Qatargas 2 is the world’s first fully integrated value chain LNG project. The project is capable of supplying 20% of UK’s natural gas demand for several years. 40 new technologies were implemented in completion of the project. 7
- The South Hook LNG Terminal in West Pembrokeshire in Wales, is part of Qatargas 2’s value chain and is collectively owned by Qatar Petroleum, ExxonMobil and Total. It is the largest LNG receiving terminal in Europe with a capacity of 15.6 MMTPA. The terminal’s five storage tanks are nearly 44 meter high and have a diameter of 95 meters, which is the largest in the world. On March 20, 2009, the ‘Tembek’ became the first ever LNG carrier to arrive at South Hook LNG. 7
- Some interesting trivia about Qatargas 2 are as follows7:
> Qatar’s North Field is estimated to hold over 900 trillion cubic feet of natural gas, that could meet all the UK’s gas needs for 250 years.
> The gas flows to Ras Laffan under its own natural pressure, without any need for pumps!
> A Q-Max at 345 metres length is 1.7 m longer than the USS Enterprise (US Nuclear Aircraft Carrier), equivalent to five Airbus A380s end to end, 45 m longer than the Aspire Tower and only 36 m shorter than the Empire State Building. One full cargo on a Q-Max can heat every home in the United Kingdom for one day (26 million homes)
> The two Qatargas 2 trains are powered by a generating unit which produces 200 megawatts of electricity, enough power to run a small city.
> The Sulfur Storage Building is shared by the entire Ras Laffan complex. At 153 m long, 115 m wide and 42 m high it could easily store four ‘747’ aircrafts.
> A Q-Max has 51,000 installed horsepower engines for propulsion which is equivalent to over 100 Ferrari F430 sports cars. - Qatargas 2 includes 30 offshore wells and three platforms in North Field offshore plant producing 2.9 billion cubic feet of gas per day and is piped to the shore via two wet-gas pipelines.8
Source:
1. ‘Chiyoda Establishes Industry-standard Materials Management System for Mega-Projects’, Integraph Website, 2012
2. The world’s largest LNG vessels – The Q-Flex design, Gard News 189, February 2008
3. Fleet List, Nakilat Website
4. Qatargas’ Chartered Fleet, Qatargas Website
5. Thompson G.R. et al. ‘Qatargas II: Full Supply Chain Overview’, LNG 14 Conference, Doha, Qatar, March 2004
6. ‘Qatar Gas II Project, Ras Laffan’, Hydrocarbons Technology Website
7. ‘His Highness the Emir inaugurates Qatargas 2’, The Pioneer Magazine, March-April 2009 Issue #124
8. ‘LNG Qatargas Latest Brochure’, Go LNG Website






















































